Magento websites are a frequent target for cybercriminals due to their widespread usage in eCommerce and the valuable customer data they handle. During a routine investigation, we discovered a malicious JavaScript injection targeting Magento websites. This malware dynamically creates a fake credit card form or extracts payment fields directly depending on the variant of the malware, activating only on checkout pages. The stolen data is then encrypted and exfiltrated to a remote server.
Overview of the infection:
Initially discovered by Weston Henry, a colleague on our team, the malware is designed to target Magento-powered eCommerce websites, specifically their checkout processes. The infection is a blend of filesystem and database malware, with the skimmer leveraging advanced obfuscation techniques to avoid detection.
 Domains Involved:
Domains Involved:
dynamicopenfonts[.]app
staticfonts[.]com
static-fonts[.]com
Two of the domains are currently on VirusTotal’s blocklist.
Code:
https://www.virustotal.com/gui/url/7c909060732cc35b47b7521d05502f093a190dce84874e6691 d95f91dfae07a7?nocache=1
https://www.virustotal.com/gui/url/77a3f4d51e5a964bf0309568c5f89d08d073c6d9aaebfb5399 48f28419d8414a?nocache=1
As of writing this article, 8 https://publicwww.com/websites/%22dy...nfonts.app%22/are infected with this malware according to publicwww.com.
How it was detected
The malicious script was flagged during a routine inspection with Sucuri’s SiteCheck. The tool identified a resource originating from the blacklisted domain dynamicopenfonts.app. Further investigation revealed its presence in two locations:
File: ./app/design/frontend/Magento/[Redacted]/Magento_Theme/layout/default.xml.
Database: The table core_config_data contained references to the malicious script.
 Infection Details
Infection Details
The malicious script was found within the <
referenceContainer> directive of the XML file, designed to load a JavaScript resource just before the closing <
body> tag. The infected code snippet is as follows:

The contents of the external script are obfuscated to avoid detection, making it challenging to identify at first glance.
Here’s the external script:

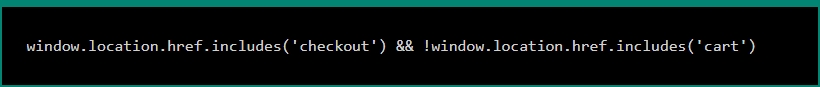
Once executed, the script activates only on pages containing the word “checkout” but excluding “cart” in the URL.
Fake Credit Card Form Example:
 Collecting User Data, Encryption and Obfuscation:
Collecting User Data, Encryption and Obfuscation:
The script is designed to extract sensitive credit card information from specific fields on the checkout page. Then the malware collects additional user data through Magento’s APIs, including the user’s name, address, email, phone number, and other billing information. This data is retrieved via Magento’s customer-data and quote models.

To protect the data and make it difficult to detect, the information is first encoded as JSON. Then, it is XOR-encrypted with the key ‘script’ to add an extra layer of obfuscation. Finally, the encrypted data is Base64-encoded to ensure safe transmission, using the following code:
 Data Exfiltration Process: Sending Stolen Information to Remote Servers:
Data Exfiltration Process: Sending Stolen Information to Remote Servers:
Once a user submits their payment details through the compromised form or hijacked fields, the malware extracts and encrypts the stolen information. This data is then sent to a remote server located at staticfonts.com using a
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_beacon.
 https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/F...king_pixel.svg
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/F...king_pixel.svg, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons

The base64 encoded URL (
aHR0cHM6Ly9zdGF0aWNmb250cy5jb20=) decodes to
hxxps://staticfonts[.]com, which is where the stolen credit card data is sent.
Beaconing technique refers to a method where a script or program sends data silently and unobtrusively from the client (e.g., the user’s browser or device) to a remote server without alerting the user or interrupting their activity. It is often used by both legitimate applications (like analytics tools) and malicious actors(like in this case). This method is stealthy and hard to detect, making it a favored tool for cyberattacks.
Conclusion:
This sophisticated skimmer targets Magento checkout pages to steal sensitive payment data, either by injecting fake forms or extracting live input fields. Its dynamic approach and encryption mechanisms make it challenging to detect. Regular security audits, monitoring unusual activity, and deploying a robust WAF are crucial to protect your eCommerce platform.
https://blog.sucuri.net/2024/11/cred...out-pages.html

